SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS, France – July 11, 2025 │ KnowMade actively tracks therapeutic mRNA innovations as part of its Therapeutic mRNA patent monitoring service. What’s new today?
Emerging Innovators in a Record-Setting Quarter for Therapeutic mRNA
The continued innovation in therapeutic mRNA is confirmed through the first half of 2025, as reflected by KnowMade’s Therapeutic mRNA patent monitoring service. During Q2 2025 alone, 272 new patent publications were identified—exceeding the 257 recorded in Q1—and underscoring an acceleration in patenting activity within the field. While BioNTech maintained strong patent publication outputs and MIT secures third position with publications covering a broader range of topics, the quarter revealed notable shifts in leadership. Indeed, the University of Texas claimed the top position with 17 new publications exclusively focused on RNA delivery. Strikingly, Sanofi, Moderna, and the University of Pennsylvania, which were dominant names past quarter, did not appear among the top three contributors in Q2 2025.
Q2 2025 also witnessed the granting of 43 new patents across key jurisdictions (US, EP, JP, KR), marking a decrease from the 64 recorded past quarter, but still reflecting high innovation maturity across the sector. As established players solidify their portfolios, new companies are also stepping onto the stage as Pinion Immunotherapeutics and Arcalis identified in Q1 2025. This quarter, a promising newcomer, Amplitude Therapeutics, was identified for the first time in KnowMade monitoring activities. With a focus on trans-amplifying RNA this emerging companies is contributing novel approaches to RNA-based therapies. This insight explores their early IP activity and the implications for the future of mRNA therapeutics.
Amplitude Therapeutics: Accelerating taRNA Innovation for Global Health
Amplitude therapeutics
Founded in 2022 and based in Boston, Amplitude Therapeutics is a seed-stage biotechnology company focused on advancing trans-amplifying RNA (taRNA) technologies. The company is currently in preclinical development phase, led by Dr. Cory Sago, with the aim of redefining RNA-based medicine. The strategy employed is to separate the replicase and antigen-encoding RNAs into two components. Amplitude’s pipeline also includes applications in monoclonal antibody delivery and protein replacement. The company has garnered strong support from leading health and venture stakeholders, securing $1 million from CEPI in March 2024 for pandemic-related taRNA research, and a $2.04 million grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to develop low-cost, taRNA-expressed biologics for infectious diseases. Additional backing from Alta Partners, ARCH Venture Partners, and Newpath Partners reinforces Amplitude’s position as a rising innovator in scalable, RNA-based therapeutics for global health.
The taRNA Advantage: Precision, Efficiency, and Scalability
Contrary to the most common platform developed, cis-amplifying RNA, Amplitude Therapeutics’ core platform leverages trans-amplifying RNA (taRNA), see the difference in the figure 1 and a comparison in the table 1. This strategy divides the RNA payload into two molecules: one encoding the replicase, and the other encoding the antigen or therapeutic protein. In contrast, cis-amplifying RNA systems encode both the replicase and the antigen on a single RNA strand, simplifying construct design but increasing RNA size, which might lead to delivery challenges and lower expression control. A detail analysis for the technology developed by a key player in cis-amplifying RNA, Arcturus Therapeutics, can be found in KnowMade insight here.
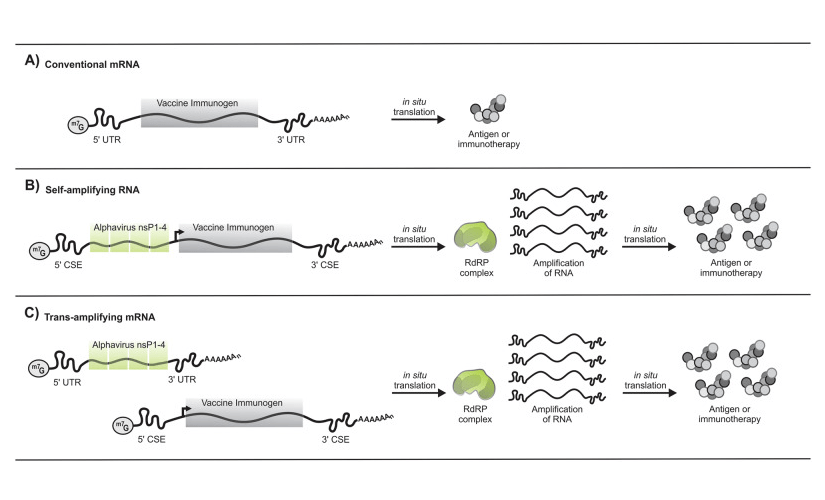
Figure 1: A comparison of the three different RNA based vaccines: mRNA, Cis-amplifyingRNA (or selef -amplifying), and Trans-amplifying RNA. Figure from (Bloom et al., 2021).
Cis and Trans amplifying RNA maintains an auto-replicative activity derived from an RNA virus and for that contains a sequence that encodes four non-structural proteins (nsP1–4) responsible of the RNA amplification. In amplifying RNAs, following in situ translation, the nsP1-4 proteins form an RDRP complex which recognizes flanking CSE sequences and amplifies vaccine-encoding transcript to result in the accumulation of the desired protein. (A) Conventional mRNAs encode the vaccine immunogen (or desired protein). (B) Cis-amplifying RNA encodes the nsP1-4 genes and the vaccine immunogen (or desired protein). (C) Trans-amplifying mRNAs use two different transcripts: a conventional mRNA encoding the nsP1-4 genes and a separate transcript encoding the viral CSE sequences and the vaccine immunogen.
| Feature | Cis-Amplifying RNA (caRNA) | Trans-Amplifying RNA (taRNA) |
| Number of RNA Molecules | 1 | 2 |
| Replicase and Antigen | Encoded on the same RNA | Separated across two RNAs |
| RNA Size | Larger | Smaller (individually) |
| Delivery Efficiency | Lower (due to size) | Higher |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Simpler (single construct) | More complex (co-formulation required) |
| Dose Flexibility | Limited | High (independent optimization possible) |
Table 1: General comparison of Cis-amplifying RNA and Trans-amplifying RNA
By decoupling replicase from the antigenic component, Amplitude’s taRNA technology provides a versatile framework for RNA therapeutics development.
Amplitude Therapeutics’ Proprietary taRNA Platform – Insights from Patent Filings
Amplitude Therapeutics’ trans-amplifying RNA (taRNA) platform is described in two recently filed international patent applications, WO2025096982 and WO2025129137 and, both published in Q2 2025 and filed respectively in November and December 2024.
The international patent application WO2025129137 describes a two-component taRNA vaccine architecture using lipid nanoparticle, as illustrated in the figure 2:
- R-NP (Replicase Nanoparticle): Encapsulates an RNA molecule encoding the replicase enzyme.
- Tr-NP (Trans-replicon Nanoparticle): Contains an RNA encoding the antigen or therapeutic payload, appended with a conserved sequence element (CSE) that enables recognition and amplification by the replicase.
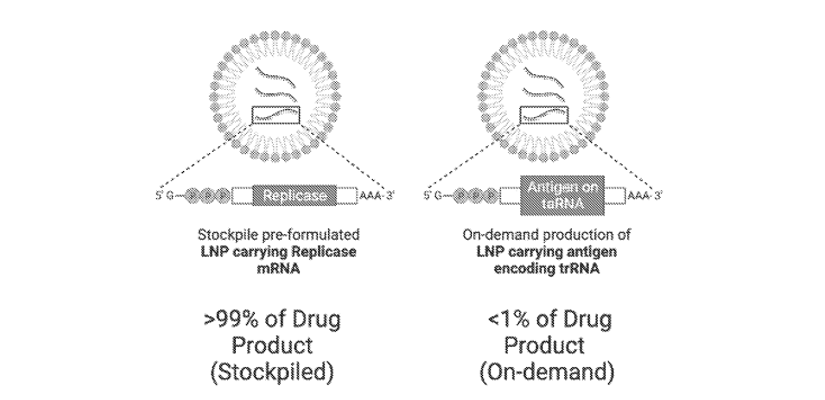
Figure 2: This figure shows an example two-component trans amplifying ribonucleic acid (RNA) (taRNA) vaccine comprising: greater than 99% lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) comprising a replicase construct encoding a replicase (and not comprising a trRNA); and less than 1% LNPs comprising a trans replicating RNA (trRNA) encoding a vaccine antigen (and not comprising a replicase construct). From WO2025129137.
According to the description of the patent application, this invention allows for a significant reduction in the amount of trRNA required for vaccine production, enabling faster and more efficient manufacturing processes. It also facilitates the stockpiling of replicase constructs, reducing the synthesis burden during vaccine development and allowing for rapid responses to emerging pathogens.
On the other hand, the international patent application WO2025096982 focuses on chemical modifications to the taRNA molecules to further enhance their translational efficiency and in vivo stability. These modifications include the use of modified nucleotides, such as pseudouridine and 5-methylcytidine, which help suppress innate immune responses and increase protein expression. In addition, the patent outlines the use of optimized untranslated regions (UTRs) and poly(A) tails to fine-tune mRNA persistence and translational dynamics in host cells.
Conclusion
Q2 2025 highlights how innovation is not limited to established players. New entrants like Amplitude Therapeutics are contributing impactful solutions to therapeutic RNA delivery and expression challenges. Its novel platforms, taRNA, reflect a strategic shift toward modular, scalable, and application-specific RNA technologies. KnowMade’s patent monitoring continues to uncover these key developments, offering critical insights into the next wave of mRNA therapeutics.
As a leader in patent analysis and monitoring, KnowMade closely follows such milestones, providing insights and solutions to support stakeholders in the dynamic mRNA vaccine landscape. For more detailed insights into these developments and how they may impact your business, please contact us.
Press contact
contact@knowmade.fr
Le Drakkar, 2405 route des Dolines, 06560 Valbonne Sophia Antipolis, France
www.knowmade.com
About the author
Elodie Bovier, PhD., works at KnowMade as a Patent Analyst in the field of Biotechnology and Life Sciences. She holds a PhD in genetic and molecular biology from the Paris Sud University. She also holds the Industrial Property International Studies Diploma (in Patent and Trademark & Design Law) from the CEIPI (Strasbourg, France).
About KnowMade
KnowMade is a technology intelligence and IP strategy consulting company specialized in analyzing patents and scientific publications. The company helps innovative companies, investors, and R&D organizations to understand competitive landscape, follow technological evolutions, reduce uncertainties, and identify opportunities and risks in terms of technology and intellectual property.
KnowMade’s analysts combine their strong technology expertise and in-depth knowledge of patents with powerful analytics tools and methodologies to turn patent information and scientific literature into actionable insights, providing high added value reports for decision makers working in R&D, innovation strategy, intellectual property, and marketing. Our experts provide prior art search, patent landscape analysis, freedom-to-operate analysis, IP due diligence, and monitoring services.
KnowMade has a solid expertise in Compound Semiconductors, Power Electronics, Batteries, RF Technologies & Wireless Communications, Solid-State Lighting & Display, Photonics, Memories, MEMS & Sensors, Semiconductor Packaging, Medical Devices, Medical Imaging, Microfluidics, Biotechnology, Pharmaceutics, and Agri-Food.cahue
