What is a patent landscape?
The purpose of a patent landscape report is to turn complex patent information into actionable insights through visual elements that make data easier to understand. It is undoubtedly a useful instrument for informed decision-making.
Patent landscaping consists in selecting and analyzing – quantitatively and qualitatively – a corpus of patents related to a specific technological field. A patent landscape analysis provides an overview of patenting activity in a specific field of technology and/or geographic area.
Why analyze patent information?
Patents can provide knowledge on levels of competitive expertise, timing and investment, in addition to providing a right to exclude. Due to the potential business and legal implications, understanding which organizations own patents, and which technological areas they cover, can have a significant impact on corporate decision-making.
A patent contains both technical, market and legal information. Therefore, patent analysis can provide meaningful information about the competitors, the level of their R&D investment, their technological roadmap and the future products and targeted markets, the key patents, and the risks and opportunities existing in the field.
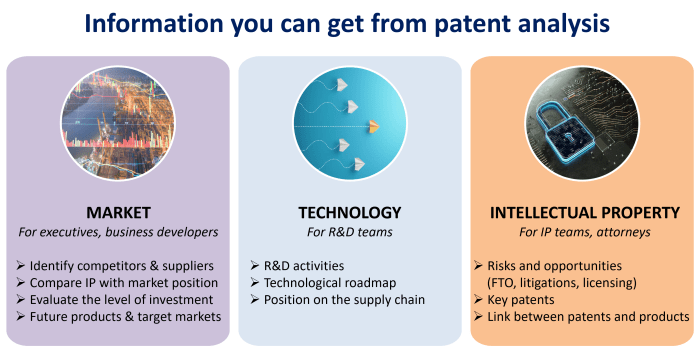
Patent intelligence is indispensable for technology-driven companies willing to gain an edge over their competitors, and helping them make strategic decisions for their technology and business development. Patent data can be utilized to spot technology trends and disruptive innovations early on and identify the technologies and markets a company is focusing on. Intellectual property (IP) analytics can reveal a company’s past drivers of success in terms of technologies and also provide a glimpse into its current R&D and future technology roadmap. Patent investigation allows to uncover newcomers and players who are still under the radar.
A patent landscape analysis helps understand the competitive landscape and technology developments from a patent perspective. It helps innovative companies, investors and R&D organizations understand their competitive environment, follow technological evolutions, and find out opportunities and risks in terms of technology and patents. It makes it possible to identify players’ R&D and IP strategies, understand where industry leaders, newcomers and start-ups are focused, and give an early view into the strategies they are pursuing and the technologies in which they are investing. A landscape analysis of patents adds an entirely new dimension to competitive intelligence, and perfectly complements market research.
Who uses patent landscape analysis?
Patent landscape analytics are used by decision makers working in R&D, innovation strategy, intellectual property, and marketing. Since businesses compete against one another, understanding the capabilities, resources and expertise associated with a competitor becomes a key component of corporate strategy. When it comes to intellectual property, decision makers must ask themselves two questions: do my competitors hold patents in any of my areas of interest? What aspects of the technology do they cover and in which countries are they enforceable?
Occasionally, companies look to move into new markets, or enter new technological areas that they do not have direct experience in previously. In that case, the patent landscape report can provide key information on the main players and the technologies in the field. This strategic data may guide the decision to invest or not in the field, developing the technology or acquiring it from others.
Industrialists commonly use IP landscape reports to assist their decision-making on R&D directions, investments and competitors. Today, public institutions also look to IP landscapes to establish a factual basis before considering high-level policy issues, especially in areas such as health and energy.
Who performs IP landscape analysis?
Only a skilled analyst can take large amounts of raw, unprocessed data to generate insight and intelligence based on the analysis conducted and the interpretation of the results.
A patent analyst should have a combination of skills and experience in patent information, legal knowledge, technology, data analysis and statistics, and presentation. All these skills are essential, because the raw patent data analysts work with is known to be difficult to grasp. It is necessary to understand it but also to represent it intelligibly to a sometimes less expert public. At all levels, a misinterpretation can lead to unfortunate consequences.
It is also important to demonstrate a general understanding of the legal aspects of the patent system, both at national and global level, especially to interpret the claims and their cryptic formulations, or to understand the patent families in various national patent systems.
Obviously, the patent analyst, in addition to mastering the techniques for searching and analyzing information, must be experienced in the area of study, knowledgeable about current technical challenges and market trends, so they can expertly interpret the results, put in perspective the IP position of players, and provide reports of high added value.
KnowMade’s patent landscape analysis service
KnowMade focuses its activity on patent landscape analysis. Find out what we do, how KnowMade was built and why we are good at what we do.
KnowMade has more than 15 years’ experience in searching, selecting and analyzing patents, and we have developed innovative, proven methodologies to carry out deep patent landscaping analysis.
Our patent landscape analyses are conducted by our patent analysts, who are highly qualified (PhD holders and Engineers) and experienced across cutting-edge technological fields, including semiconductors, batteries, biotechnologies and agri-food. KnowMade’s analysts combine their strong technological expertise and in-depth knowledge of patents with powerful analytical tools and methodologies to turn patents into business-oriented patent landscape analysis reports for decision makers. Our analysts provide an expert opinion, conclusions and perspectives based on their knowledge of the topic in question, and not just data. Our team is always on hand to ensure the client’s needs are met and to make any necessary adjustments to the patent search and analysis process.
What can you learn from our patent landscaping?
Our patent landscape analysis allows you to understand, anticipate and evaluate the competitive landscape and technological developments. It gives you a comprehensive competitive and technology landscape for a specific domain, and enables you to know where you stand amongst your competitors.
Our patent landscaping allows you to…
- Get to know the key IP players, their key patents, their IP/technology strategy and their future intent
- Identify the historical players who are still active and those who are now inactive
- Identify the players increasing their patent activity, and those decreasing or abandoning theirs
- Spot the newcomers, even those who are still under the radar
- Find out the levels of competitive expertise and R&D investment
- Uncover who has the strongest patent portfolio, and who is making new development efforts
- Follow the technological trends and identify emerging technologies
- Find out the major technological thrust areas
- Know which technologies your competitors are pursuing
- Uncover who is making IP decisions to achieve a strong future market position
- Spot the players you need to be watching
- Benchmark patent portfolios and find out competitors’ strengths and weaknesses
- Compare players’ IP and market position
- Identify IP collaboration networks between key players
- Identify the key patents and the key technical solutions that address hot technical issues
- Identify the technology gaps (whitespaces) that you can exploit against your competitors
- Understand the risks of litigation, opposition and infringement in the area
- Identify free technologies which can be used safely and mitigate the risks of patent infringement
- Uncover new opportunities in terms of technologies and patents
- Identify technologies to acquire and potential R&D partners
Content of our patent landscaping
Methodology for patent searches, selection and analysis
We are fully transparent about the methodologies and databases we use to carry out the analysis. We provide the search strategy, keywords, search queries, and methodology details explaining the criteria by which patents are defined as relevant for the study and the reason they have been selected or excluded.
Patent information is extracted from the FamPat worldwide patent database (Questel-ORBIT), which provides 100+ million patent documents from 100 patent offices (USA, Japan, Europe, South Korea, China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore, etc.).
The relevant patents are hand-picked by an expert in the required technological field. A two-step methodology is used to establish the patent corpus: a set of complex search queries are used to extract raw corpuses from the patent database, then a manual screening of raw results is performed to eliminate patents considered irrelevant to the field. In our search strategy, we use, inter alia, keyword analysis applied to the title, abstract, claims and description of the patents, the patent class analysis (IPC, CPC), and the citation analysis. This is an iterative process in which we refine the search queries and strategy. Similarly, the selected patents are then manually categorized by technology, by application, or according to value chain segments.
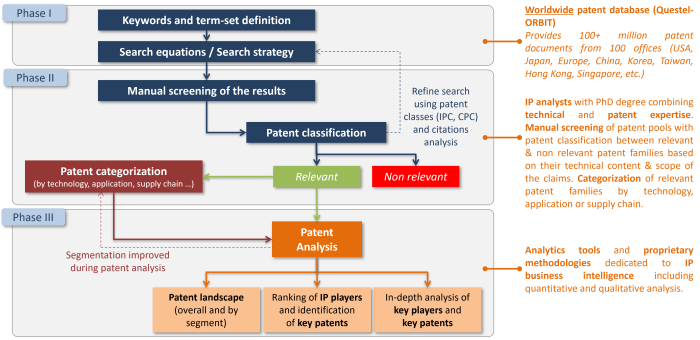
Quantitative and qualitative analyses for the whole corpus and for each segment
- Ranking of patent assignees according to the number of their patent families, patent applications, granted patents, pending patent applications, etc.
- Time evolution of patent publications/filings by assignee and segment
- Most active patent applicants over the last few years
- Main patent assignees by company typology, country of headquarters, segment, etc.
- Current legal status of patents (granted, pending, abandoned, expired) by assignee and segment
- Geographic coverage of patents and patent applications (filing countries) by assignee and segment
- Patent assignees versus Segments matrix
- Mapping of collaborative networks (co-filings, transfer of IP rights)
- Patent litigations, third-party observations, oppositions, court cases or transactions that have involved patents
- Benchmark of patent portfolios (size, enforceability, current patent activity, prior art contribution, geographical coverage, technical coverage, technology overlap/difference, blocking potential, etc.)
- Identification of key patents (critical technology blocks, influential patents, blocking patents, valuable patents)
- Focus on top IP players’ patent portfolios (IP profile): summary of portfolio (patenting activity, patent legal status, geographical coverage, technology coverage, IP strength), description of key patents and recent patenting activity (technology, approach, invention purpose, basic structure/function and its effect, etc.). Such IP profiles aim to give a view, through patent analysis, into the R&D and IP strategies the players are pursuing, where they are focused, the technologies in which they are investing and products they are likely making/marketing.
Key players and key patents
There are many methods and arguments to assess whether a patent is of high quality, valuable or “key”. At KnowMade, key patents and key IP players are identified using scientifically validated value metrics that provide an objective measure of the importance of a patent and the IP strength of an organization. We have developed unique methodologies based on the assessment of intrinsic patent indicators and supplemented by expert review of the patented technology.
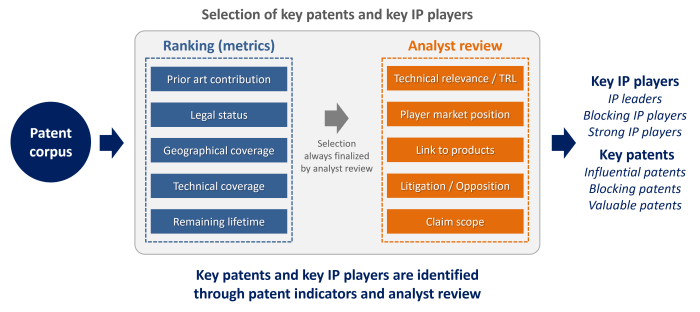
Key patents are identified according to the following criteria:
- Patent legal status (granted, pending, expired, abandoned)
- Patent geographic coverage (filing countries)
- Prior art contribution (citations received by the patent)
- Technology coverage and claims scope
- Competitive impact (number and typology of patent applicants citing the patents)
- Remaining lifetime of the patent (expiry date)
- Patents involved in litigation and/or opposition
- Licensed patents
- Patents likely used in a product
These metrics are useful tools to identify the companies that appear to be the strongest and most relevant in the field, and single out a few patent families that seem particularly relevant. But ultimately, only a careful examination of every single patent by legal and technical experts could provide a more accurate assessment of a company’s patent portfolio, and the relevance to the field of a given family of patent applications.
Business-oriented PDF report for decision makers working in R&D, IP departments, strategy and marketing
Our patent landscape reports include the methodologies, analyses and our analysts’ interpretations, conclusions, and perspectives, in view of the objectives that led to the ordering of the report. We provide a high added value and concise report of the key trends and observations in the area of study. We aim to organize large amounts of data into a trustworthy story and present the results in an engaging manner tailored to the readers, mixing information related to intellectual property, technology, and market.

Executive summary
Our patent landscape reports include an executive summary that, among all the other content, is the one to read carefully. It contains the key information to remember and highlights key points from the analyst’s point of view.
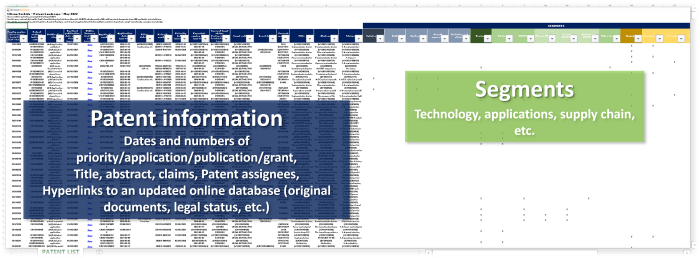
Useful Excel patent database
In each patent landscape report, we enclose a comprehensive Excel database which contains the following information for each patent family selected for the report:
- Publication number, application number, and priority number of every member of the patent family
- Title
- Hyperlink to an updated database (with access to original documents, their current legal status, etc.)
- Current legal status
- Abstract
- Patent assignees
- Segments