
What are the current patenting activities, and how can they support players’ strategies to strengthen their IP portfolio, secure their position, and conquer new market shares?
Publication February 2024
| Download Flyer | Download Sample |
KEY FEATURES

- PDF>110 slides
- Excel file>11,300 patent families
- Global patenting trends, including time evolution of patent publications, countries of patent filings, etc.
- Main patent assignees and IP newcomers in the different segments of the supply chain.
- Key players’ IP position and the relative strength of their patent portfolio.
- Focus on the Chinese ecosystem.
- IP analysis of the main technologies:
- SAW filters
- BAW filters
- LBAW filters (incl. XBAR)
- Multiplexers & RF FEM using acoustic filters
- Focus on recent key innovations for SAW, BAW, composite piezoelectric substrates, etc.
- IP profile of key players and Chinese newcomers (patent portfolio overview, technical coverage, geographical coverage, etc.)
- Excel database containing all patents analyzed in the report, including patent segmentations and hyperlinks to an updated online database.
KnowMade’s experts also produce an RF acoustic wave filters monitor and an RF FE Module and Components monitor.
The need of new solutions for high bands
Since the 1990’s, the acoustic filter industry has been divided into two main technologies: surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters for the lower bands and bulk acoustic wave (BAW) filters for the higher bands. This market and the players were well-established, and their products, technologies, and know-how were protected by large and strong intellectual property (IP) portfolios. Murata and Skyworks were leading the SAW patent landscape, while Broadcom was leading the BAW one. The expansion of cell phone services and networks drove the need for progressively wider and higher frequency bands. 5G applications, for instance, require frequencies in the sub-6GHz range (e.g., 3.3–3.8 GHz (B78), 3.3–4.2 GHz (B77), 4.4–5.0 GHz (B79)) as well as mm-wave bands (e.g., 24.25–29.5 GHz (B257, B258, B261), 37–40 GHz (B260)). While reaching higher frequencies is one part of the challenge, the other part is to provide RF filters that not only work at higher frequencies, but also offer wider absolute and relative bandwidths.
Currently, SAW and BAW devices fulfill the requirements for bands below 3GHz. However, when it comes to the 3–5 GHz range, numerous issues arise. SAW devices require increasingly narrower electrodes, which result in higher losses, reduced power handling, and more expensive lithography. BAW devices likewise have relatively small piezoelectric coupling and lack the capacity to support the wider bandwidths required. Therefore, new solutions that address losses, power, thermal issues, and bandwidth needs above 3 GHz will be attractive.
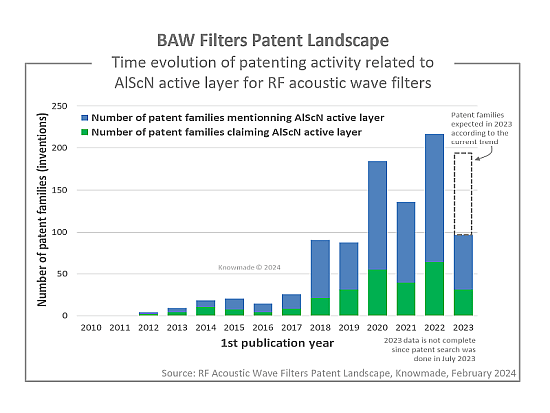
To overcome these limitations, players are looking for new technologies. New solutions include the development of BAW with a ScAlN or Sc-doped AlN piezoelectric film in order to enhance the electroacoustic coupling characteristic. On the other hand, the development of new composite substrates has opened new doors for the SAW segment. Last, laterally excited BAW (LBAW) technology has also entered the race.
Many players have seen this evolution as a good opportunity to enter this lucrative market and explicitly desire to be the upcoming provider of the next generation of RF filters for 5G. Newcomers as well as established players have thus entered a fierce race in which IP can be a major tool to support their strategy. Furthermore, the US vs. China technology battle has led to the development of a national supply chain in China. All these elements are adding up to result in a very dynamic and competitive industry.
In this context, the RF Acoustic Wave Filters Patent Landscape report aims to understand the current IP activities and how they can support the market strategies of players. The analysis of more than 25,000 patents offers a unique view of how players can leverage their IP to secure their position or conquer new market shares.
Understanding the main trends, the key players’ IP position and IP strategy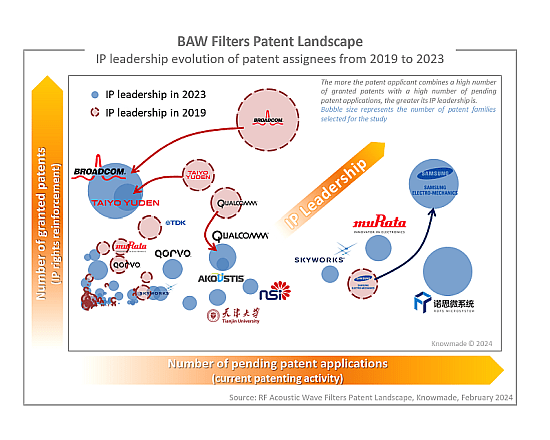
In this report, we have manually selected more than 11,000 patent families (inventions) related to SAW filters, BAW filters, and multiplexers and RF front-end modules using them, and provide a general overview of today’s IP landscape global trends and dynamics. Through patent analysis, we describe the position of players along the supply chain, unveil their strategies to strengthen their IP portfolio, highlight their capability to limit other firms’ patenting activity and freedom-to-operate, identify promising new players, and forecast what would be the future IP leaders. Furthermore, this report provides an understanding of players’ IP position on promising technologies. The main players involved in the development of new technologies are identified, and the main solutions to address these challenges are described.
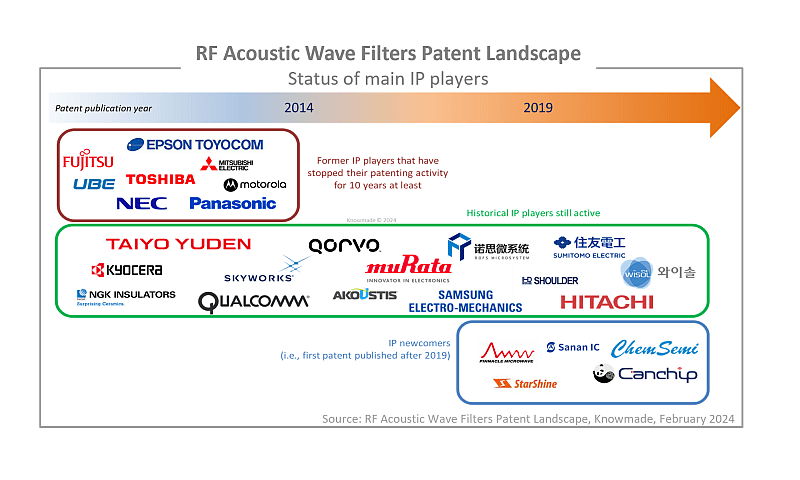
The analysis highlights a significant difference between the SAW and BAW IP landscape. On one hand, the development of SAW filters has reached a high level of maturity, and IP players have started to look at module design and filters architecture. Vertical innovators are controlling the IP landscape and will be difficult to challenge. On the other hand, the BAW IP landscape is characterized by intense competition. The recent decline in patent activity from Broadcom and Taiyo Yuden, paired with the rise of the AlScN piezoelectric layer, has created new opportunities that numerous Chinese players and established SAW players are not going to miss!
What is the position and strategy of Chinese IP players?
The report provides an understanding of the current IP positions of major Chinese players.
We have identified the most noticeable Chinese patent owners and provide a first view of how they are developing their IP in order to establish a national supply chain. Additionally, the IP analysis allows us to pinpoint Chinese players who are implementing a global IP strategy by extending their patents abroad. Lastly, the report offers a comprehensive overview of the patent activity of the most noticeable Chinese players, providing insight into their recent technological advancements.
 How can IP support the development of new filter technologies?
How can IP support the development of new filter technologies?
The 5G requirements led to the development of several new technologies. The most noticeable being related to the substrate and materials used in the filters. Composite piezoelectric substrates and AlScN have become two of the most promising technologies to fulfill the requirements. Filing patents related to these technologies seems necessary to secure the technology for the next 10 years. KnowMade provides a first status of this specific IP segment to understand which players have the strongest IP portfolio that can be used to hamper the freedom to operate of the competition in the coming years.
IP profile of key players
In a dedicated section, we focus on the IP portfolios held by key players (Murata/Resonant, Skyworks, Qualcomm, Taiyo Yuden, Samsung Electro-Mechanics, ROFS Microsystem, Akoustis, Qorvo, Kyocera, Wisol) and Chinese IP newcomers (MEMSonics, EpicMEMS, StarShine, Sanan IC, Sappland Microelectronics).
Useful Excel patent database
This report also includes an extensive Excel database with all patents analyzed in this study. This useful patent database allows for multi-criteria searches and includes patent publication numbers, hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), priority date, title, abstract, patent assignees, and segments (SAW, BAW, LBAW/XBAR, multiplexer & RF FEM using them).
Companies mentioned in the report (non-exhaustive)
Murata, Taiyo Yuden, TDK Epcos, Skyworks, Kyocera, Qualcomm, Broadcom, Hitachi, Toshiba, Toyo Communication Equipment, Samsung Electro Mechanics, Qorvo, Seiko Epson, Oki Electric Industry, LG Innotek, NDK, NEC, Epson Toyocom, Sanyo Electric, Samsung Electronics, NGK Insulators, Philips, Intel, Japan Radio, Nokia, Thales, Advanced Saw Products, Motorola, Wisol, Ube Industries, Mitsubishi Electric, Sumitomo Electric Industries, LG Electronics, China Electronics Technology (CETC), Alps Electric, Tianjin University, Toko, Sappland Microelectronics Technology, Zenith Radio, Texas Instruments, Sony, Intellectual Ventures Holding, Resonant, STMicroelectronics, Institute of Acoustics – Chinese Academy of Sciences, Mitsubishi Materials, CEA, Shoulder Electronics, and more.
