Discover the intricacies of mRNA and its rapidly advancing technologies with the assistance of KnowMade’s patent expertise.
- Gain access to valuable insights on the latest mRNA patent news at no cost.
- Delve deeper into the field with our comprehensive reports.
- Stay at the forefront of research and development and intellectual property advancements through our monitoring services.
Insights
SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS, France – January 16, 2026 │ This quarter, KnowMade’s Therapeutic mRNA patent monitoring service highlights PopVax as an emerging innovator driving multivalent mRNA [...]
SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS, France – October 17, 2025 │ This quarter, KnowMade’s Therapeutic mRNA patent monitoring service reveals two emerging players shaping the next wave of [...]
SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS, France – July 16, 2025 │ KnowMade actively tracks therapeutic mRNA innovations as part of its Therapeutic mRNA patent monitoring service. What’s new [...]
SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS, France – July 11, 2025 │ KnowMade actively tracks therapeutic mRNA innovations as part of its Therapeutic mRNA patent monitoring service. What’s new [...]
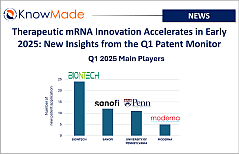
SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS, France – April 28, 2025 │ The therapeutic RNA landscape continues to evolve with a robust pace of innovation. The latest Q1 2025 [...]
SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS, France – February 04, 2025 │ KnowMade actively tracks therapeutic mRNA innovations as part of its Therapeutic mRNA patent monitoring services. What’s new [...]
Reports
 |
 |
 |
| Self-amplifying RNA vaccines Patent Landscape Analysis 2023 | mRNA Cancer Therapies Patent Landscape Analysis 2022 | RNA vaccine Patent Landscape 2021 |
Monitor
 |
| Therapeutic mRNA Patent Monitor |