SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS, France – October 03, 2025 │ With the launch of Cetaphil’s new Skin Activator Hydrating & Firming Line, Galderma makes a step ahead to address skins affected by dermatoporosis. KnowMade deciphers this new formula.
Galderma at a glance
Originally founded in 1981 as a joint venture between Nestlé and L’Oréal, Galderma became an independent entity in 2019 under a private investor consortium. Headquartered in Zug, Switzerland, the company, exclusively focused on skin health and aesthetics, is a leader in global dermatology. Galderma invests heavily in research, development and strategic partnerships to drive innovation in dermatology. Its R&D network spans Switzerland, the USA, Canada and Sweden, with advanced manufacturing facilities in Europe and North America. Using a strategy oriented through injectable aesthetics, dermatological skincare and therapeutic dermatology, the company offers a large portfolio of brands composed of innovative products.
The company owns more than 800 patent families, mainly filed prior to 2017. Since 2018, a slow down of Galderma IP activity has been observed, which can be the result of the internal restructuring operated by the company in 2017. Indeed, with closing of the R&D activity in Sophia-Antipolis (France), Galderma has reoriented its research activities and reduced drastically its IP activity. Therefore, its IP portfolio is mainly not active with only 10% of its portfolio in terms of patent families still under examination and 70% dead. The company shows a desire for a broad coverage with a significant percentage of WO applications.
In recent years, Galderma has made pipeline innovations including ALASTIN’s Restorative Skin Complex to promote skin regeneration or Relfydess® to improve facial wrinkles and has conducted active clinical programs in skin disorders and chronic pruritus. With the new Skin Activator line from Cetaphil, Galderma stands out to combat dermatoporosis.
Waking up sleeping surface skin cells: the promise of Galderma’s new Skin Activator technology
A focus on dermatoporosis
Dermatoporosis is a skin disorder, characterized by thin and fragile skin naturally occurring with aging. As keratinocytes lose proliferative capacities, the epidermis becomes thinner, while underneath in the dermis, fibroblasts, collagen and elastin, the extracellular matrix elements are drastically reduced (Figure 1). Skin flexibility is altered and all these changes lead to reduced skin strength and elasticity.
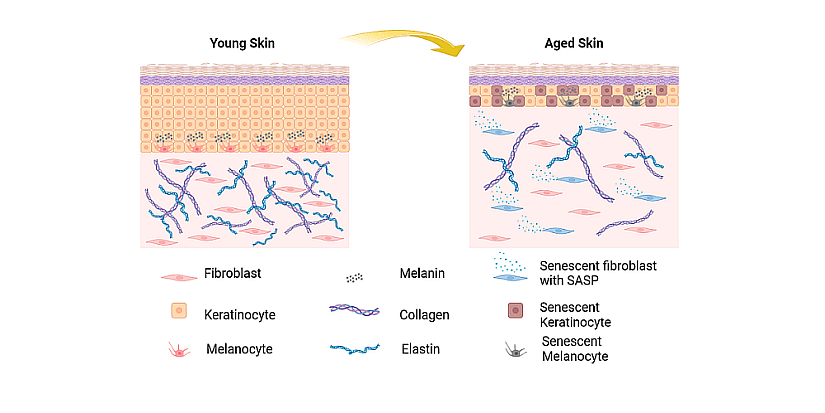
Figure 1: Schematic representation of skin aging. From Konstantinou et al., 2024.
Usually associated with aging as an intrinsic process and a primary risk factor, dermatoporosis can also be accelerated by various extrinsic and secondary factors, such as photodamage (UVA and UVB repeated expositions), genetic inheritance, corticosteroid use and lack of exercise.
Cellular senescence is a known contributor to dermatoporosis, as senescent fibroblasts no longer produce collagen and elastin, but enter a senescent-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in which they secrete high levels of inflammatory cytokines, immune modulators and proteases that create an inflammatory environment. In the epidermis, senescent keratinocytes and melanocytes also contribute to the onset of dermatoporosis. Considered as “sleeping cells”, these dormant cell types could be woken up to decrease inflammation and stimulate cellular turnover.
Managing cellular senescence with active components
Waking up sleeping cells is the strategy chosen by Galderma. For that purpose, the company has associated mandelic acid, a skin-friendly low pH compound known to stimulate cellular turnover, with Centella asiatica, a medicinal herb rich in triterpenes known to exert therapeutic effects on wound healing and dermatological disorders such as atopic dermatitis. The patent application WO2024/163456 precisely describes the effect of this topical composition on components of dermatoporosis. Administered at non-cytotoxic microdoses to primary adult normal human epidermal keratinocytes, these two components act synergistically to significantly downregulate the expression of SASP cytokines, particularly interleukin 8 and 1B (IL8 and IL1B) (Figure 2).
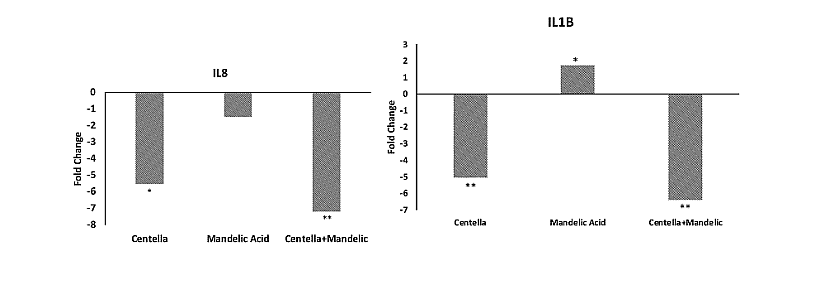
Figure 2: SASP-associated gene synergy in keratinocytes. From WO2024/163456.
The graph illustrates the changes in gene expression for keratinocytes treated with Centella asiatica (0.005%), Mandelic acid (0.05%) or a combination of both for 72h. Using RNA-sequencing techniques, differentially expressed genes were identified and compared with untreated keratinocytes to determine fold changes.
Using similar techniques, the inventors also highlight a synergistical effect of Centella asiatica and mandelic acid on the downregulation of inflammatory-associated genes, particularly matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2), heat shock protein A8 (HSPA8) and NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (NFKBIA), in keratinocytes. In dermal fibroblasts, the combination of the two components leads to an upregulation of the expression of genes related to cell cycle regulation. According to the inventors, Centella asiatica and mandelic acid can act synergistically to reduce senescent cells activity in keratinocytes and increase dermal fibroblast cell turnover. Moreover, when topically administered to skin explants, a formulation (Table 1) containing mandelic acid and Centella asiatica encapsulated into the inner core of liposomes to ease its release to the skin different layers (stratum corneum, epidermis, dermis) stimulates senescent cell removal in both the dermis and the epidermis.
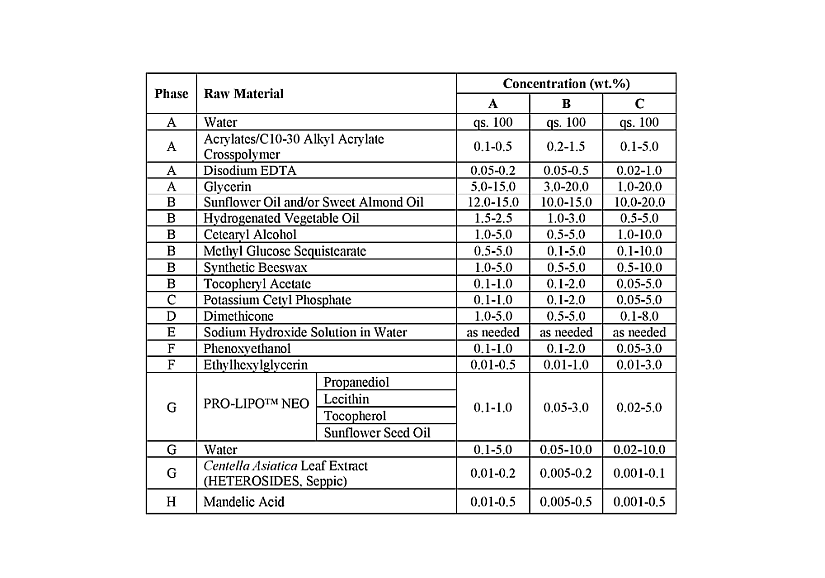
Table 1 : Exemplary topical compositions containing Centella asiatica extract and mandelic acid. From WO2024/163456.
According to the inventors, this invention offers an innovative approach to limit cellular senescence in skin cells and provides a new alternative for managing dermatoporosis.
Filed in January 2024, this application is still pending in many countries. Regarding the procedure, the International Search Authority’s written opinion has concluded that claim 1 (directed to a topical composition based on a Centella asiatica extract encapsulated in liposomes, combined with an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) at pH<5) is novel, as no single prior art document discloses this exact combination of bioactive components. Nevertheless, this composition is not recognized as inventive. Indeed, the examination of prior art, patent FR3108037 owned by FAREVACARE, in particular, would render the solution obvious. To increase its chances of grant, the claim could be restricted to more specific and experimentally supported features, such as limiting the AHA to mandelic acid, defining a Centella asiatica extract enriched in triterpenes encapsulated in well-characterized liposomes, specifying a narrow pH range (4.0-4.5) and integrating the demonstrated synergistic effect on senescence biomarkers (such as SASP cytokines). Taking together, these adjustments could better support inventive step and clearly differentiate the invention from the prior art.
According to the International Search Authority, clarity and support also need to be reinforced in several claims in order to present a better definition of biomarkers and biological mechanisms involved and enrich the description of Centella asiatica extraction methods.
Furthermore, it should be noted that the European application derived from WO2024/163456 has been deemed withdrawn by the EPO, but this is a non-final decision and so must be followed if relevant.
As the timeline remains very early in the examination procedure, it is too soon to predict the future of protection of this patent application.
An innovative formulation improving visible signs of dermatoporosis
The incorporation of microdoses of mandelic acid and Centella asiatica within a complete formulation designed for sensitive and aging skin can address early signs of dermatoporosis (Widgerow et al., 2025). In a clinical study published by authors affiliated with Galderma, this formulation was used under normal conditions of application (twice daily) by participants aged 65 years and older with self-reported sensitive skin and dermatoporosis signs. Over a period of 12 weeks, different assessments were performed, including skin hydration, skin barrier transepidermal water loss, skin thickness, cutaneous tolerability, clinical scoring of roughness and dryness. As early as 7 days, skin hydration and barrier function are significantly improved, and these effects are maintained over time. Skin thickness appears gradually increased with improvements in both the dermis and epidermis. Moreover, the cream improves skin dryness and tactile roughness on treated areas as participants report as early as 7 days of topical application (Figure 3).
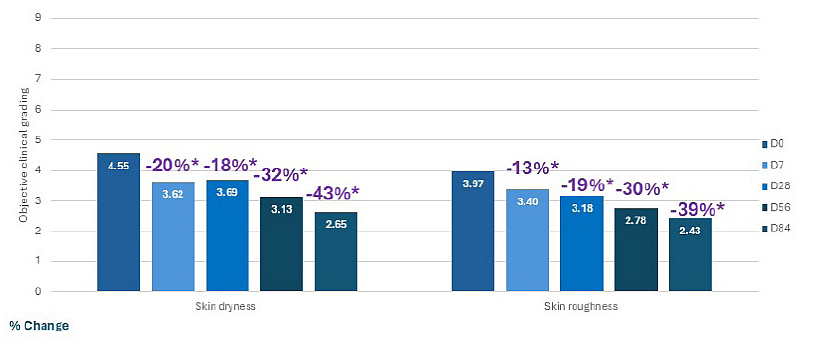
Figure 3: Evaluation of improvements in skin dryness and roughness throughout 84 days of topical application of Galderma’s active formulation. From Widgerow et al., 2025.
The graph illustrates the objective clinical grading of skin dryness and roughness as a percentage of change after application of a cream formulated with microdoses of mandelic acid and Centella asiatica. Over a period of 84 days of topical application on both arms and one leg (twice daily), 54 participants aged 65 years and older self-evaluated roughness and dryness of their skin through a clinical scoring from 0=very soft skin to 9= not soft skin, very rough texture.
After 1 week of topical application, participants also report an improvement of skin smoothness and skin quality by over 90%. This observation is maintained over time, as participants rate over 90% an improvement of their skin overall appearance, hydration, smoothness, firmness and quality after 4 weeks and 12 weeks. Regarding product tolerability, no related adverse effects and no significant changes in cutaneous aspect (erythema, oedema, irritation, dryness or peeling) were reported.
This formulation offers a new and innovative cosmetic solution specifically adapted to aging patients with early visible signs of dermatoporosis. It maintains skin thickness in a large variety of sensitive skin types and is associated with good local tolerability and high level of satisfaction. Nevertheless, the potency of this formulation could be reinforced by a direct comparison with a standard hydration cream to highlight even more the beneficial effects of mandelic acid and Centella asiatica on dermatopotic skins.
Launching of Galderma’s new Skin Activator Hydrating & Firming line
Within Cetaphil, its recognized dermatologist recommended skincare brand, Galderma has recently launched in the USA, a new fragrance-free, non-comedogenic and hypoallergenic Skin Activator Hydrating & Firming line (Figure 4). Formulated for improving the appearance of aging skin, this product line offers a new and innovative solution in the skincare segment of advanced hydration. The Skin Activator technology works as a “wake-up” call for inactive surface skin cells. Enriched with encapsulated Centella Asiatica (CICA) and mandelic acid, the formulation helps restoring the skin’s hydration barrier and promotes surface cell renewal. This allows a reduction in dullness and even texture by visibly plumping and firming fine lines. The formula is proven to restore a more youthful look with visible hydration benefits within four weeks. Moreover, 87% of users affirm their skin looks younger after one week of use.

Figure 4: Hydrating and Firming skincare line from Cetaphil. From Galderma.
Conclusion
The innovation described in the patent application WO2024/163456 aims to limit skin cell senescence and provide a novel treatment option for dermatoporosis, a new research area Galderma has decided to focus on. This application is the only one related to dermatoporosis so far. Filed early in 2024, the application is still pending internationally, and the International Search Authority has found that the first claim is novel but non-inventive in view of prior art. Narrowing the claim could allow the acknowledgement of an inventive step for the object of the claims by national offices.
With this innovation, Galderma takes a stand in the way to approach skin longevity. By preserving surface skin health at the cellular level, this Skin Activator Hydrating and Firming line is a routine developed to strengthen and revitalize skin, especially when it comes to aging. The concept of skin longevity, with the aim of reactivating dormant cells, is a thematics developed by cosmetics companies over the last five years. By using senolytic agents, designed to remove senescent cells, or senomorphic agents, to alter their phenotype, industrials are able to develop cosmetic formulations specially designed to prolong skin longevity and attenuate the effects of skin aging. Targeting cellular senescence, particularly through the reactivation or modulation of dormant cells, has become a growing area of interest in the cosmetics industry since 2020. While it is not yet a mainstream approach, several major players and ingredient suppliers are already investing significant resources to explore these pathways.
Press contact
contact@knowmade.fr
Le Drakkar, 2405 route des Dolines, 06560 Valbonne Sophia Antipolis, France
www.knowmade.com
About the author
Céline Gaudel, PhD., works at KnowMade in the field of Biotechnology and Life Science. She holds a PhD in Molecular and Cellular Biology from the University of Nice Sophia-Antipolis (France). She previously worked in academic research in France and Ireland and has a background in skin science and cosmetic ingredients.
About KnowMade
KnowMade is a technology intelligence and IP strategy firm specializing in the analysis of patents and scientific publications. We assist innovative companies, investors, and research organizations in understanding the competitive landscape, anticipating technological trends, identifying opportunities and risks, improving their R&D, and shaping effective IP strategies.
KnowMade’s analysts combine their strong technology expertise and in-depth knowledge of patents with powerful analytics tools and methodologies to transform patent and scientific data into actionable insights to support decision-making in R&D, innovation, investment, and intellectual property.
KnowMade has solid expertise in Semiconductors and Packaging, Power Electronics, Batteries and Energy Management, RF and Wireless Communications, Photonics, MEMS, Sensing and Imaging, Medical Devices, Biotechnology, Pharmaceuticals, and Agri-Food.
